If you want to use MailHog ( https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog ) on your Google Compute Engines (GCE) you probably have to create a new VPC firewall rule in your project. In this post, I will skip the installation and configuration part of MailHog with Supervisord, because there are so many different ways to set up MailHog.
|
1 2 3 |
# Mailhog wget -q https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases/download/v0.2.0/MailHog_linux_amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/mailhog && chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/mailhog wget -q https://github.com/mailhog/mhsendmail/releases/download/v0.2.0/mhsendmail_linux_amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/mhsendmail && chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/mhsendmail |
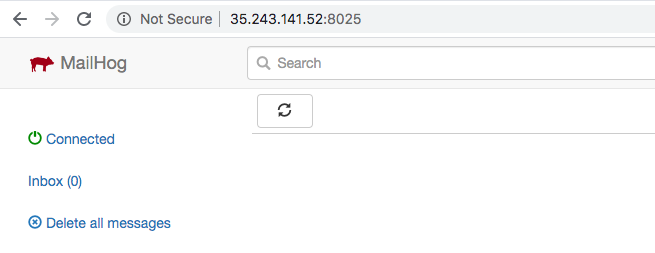
By default, the MailHog interface is running on port 8025.
Once the MailHog process is up and running, you probably won’t be able to access your server on port 8025. This is because those ports are not defined in VPC. In order to get access from outside, you must create a new firewall rule in your GCE project. This can be done in the Google console or simply via the command-line. Here is how I created a new rule ” custom-allow-mailhog ” for port 8025.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
gcloud compute firewall-rules create custom-allow-mailhog --allow tcp:8025 --priority=65534 --description="Mailhog on port 8025" --direction=INGRESS Creating firewall...⠶Created [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/tobiasforkel/global/firewalls/custom-allow-mailhog]. Creating firewall...done. NAME NETWORK DIRECTION PRIORITY ALLOW DENY DISABLED custom-allow-mailhog default INGRESS 65534 tcp:8025 False |
Once the rule has been created, you should be able to open the interface of MailHog.